In many cases, before the final color finish of the surface, it must be primed. For such purposes, you can use the base paint, but this is in most cases irrational. After all, a more expensive coating component is consumed and the main target task is not solved - preparing the surface for painting. How to calculate the primer consumption and how much it needs to be purchased?
- Why do you need a primer
- Types of primers and features of their application
- How to calculate the need
- Specific consumption of different primers

Why do you need a primer
The fundamental difference between the paint and the primer is that staining creates the final color solution of the treated surface, and priming ensures the quality of this process. Thus, a primer is necessary so that the subsequent coat of paint does not lag behind the original surface over time.
It is rare when the painted layer is dense and monolithic. The exception is metals, as well as some (very limited quantities) of plastics and composites. All other materials - concrete, wood, plaster - are porous to one degree or another. Direct staining of such materials only leads to overuse of paint. The durability of such a coating on the walls also leaves much to be desired: over time, it peels and lags.
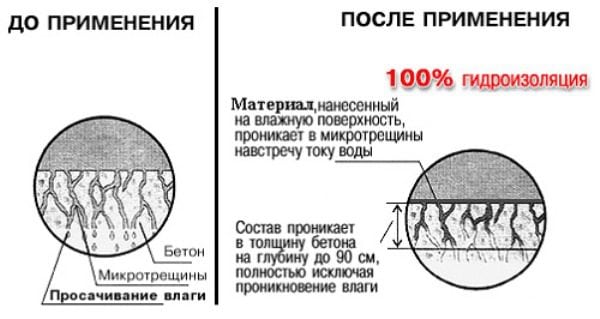
In such cases, they prefer to blame the paint, although it has nothing to do with it. The reason is different - high-quality preparation for staining was not carried out. And this is not only cleaning the walls from traces of dirt, dust, grease, but also filling all available pores. It is the last function that various primer compositions perform.
The second, no less important, task of priming is to increase the strength of the initial surface during subsequent work with it. Both plaster and putty are very fragile materials: they can easily crumble under various mechanical influences. Over time, their strength is further reduced. Therefore, the primer is also intended for high-quality bonding of various components of the finishing compositions to each other.
Finally, a primer is necessary in order to protect the surface from harmful external influences, for example, from fungus formation, decay, etc. Paint usually does not contain components of protection against mold - it has a different task. But the primer compositions, discreet in terms of color and expressiveness, just provide the necessary resistance to high humidity, temperature fluctuations.
to contents ↑Types of primers and features of their application
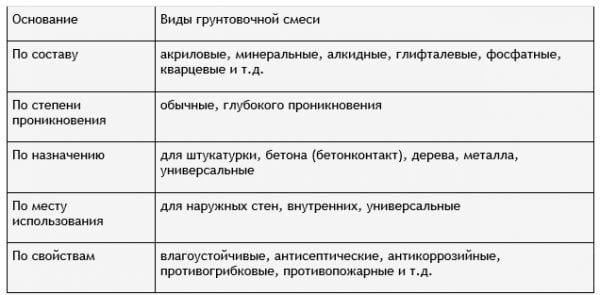
In accordance with the type and technological characteristics of the treated surface, these types of polymer primers are distinguished:
- Alkyd, intended mainly for preparation for painting wood, including the facades of wooden houses. Sometimes they are also used for metal surfaces. Since alkyd resins are part of such primers, it is not recommended to use a different type of paint in the future. Such primers are not applied to plaster or gypsum surfaces. Not recommended for internal use, as it is quite toxic.
- Epoxy, which is used to process ordinary steel, tin, chemically resistant plastic.Such primers provide the highest quality adhesion of epoxy paint to the surface, but they completely fill all the pores in the starting material, therefore they are suitable only for processing inorganics, which practically do not respond to changes in external conditions. Processing pipes, house facades - the most appropriate areas of application of epoxy primer.
- Acrylic, which are considered the most versatile. They are ideal for all types of paints and original surfaces, both internal and external. Metal, bituminous compositions, plaster lend themselves perfectly to priming with such materials. Deep penetration acrylic primer, which is recommended for facade building elements, is even more effective. However, it is not advisable to prime metal with such compositions, since they do not contain anti-corrosion components.
The fundamental feature of all primer compositions is that they show their maximum effectiveness only when subsequently the surface is treated with paint of the same composition. This is not surprising, since the main component of both types of coating is the same, and therefore the adhesion is expected to be of higher quality.
to contents ↑The composition of any primer also includes a number of excipients: fillers, adhesives, resins, neutral coloring pigments, and sometimes oils.
How to calculate the need
The need for a primer is determined in the same way as for paint. Worse, when it is not enough, but for the sake of this it is impossible to reduce the intensity of primering: deterioration in the quality of this operation will lead to the fragility of the painted coating (especially for textured, quartz putties), which ultimately results in unnecessary financial costs.
Primer consumption per 1 m² of surface is the main way to determine the need for a given coating. In this case, the type of primed surface is of decisive importance. For example, the consumption of deep penetration material turns out to be higher than that of a conventional one, but, ultimately, the adhesion to paint increases markedly. Given that the price of the primer is lower than the paint, the resulting household benefits are obvious.
Primer manufacturers usually indicate the specific consumption of the composition on the package. But these values are indicative and depend on the specific conditions of work with this composition, including external values of temperature and humidity. For example, it is impossible to prime the facade surfaces at temperatures below 5-10 ° C, and the primer of rooms with high humidity (in particular, bathrooms) is possible, but does not guarantee the rated performance of the adhesive, which will subsequently be glued to the walls of ceramic tiles.
Thus, the calculation of the need for primer material depends on:
- configurations of the primed surface (with its complication, the flow rate increases);
- specific composition and purpose of the primer;
- composition of the initial surface;
- type of subsequent processing;
- external temperature and humidity conditions (especially important for work on the facades of houses);
- a method of applying a primer to plaster, polymeric materials, pipes and other surfaces.
In the future, we will consider all recommendations regarding such a parameter as primer consumption per 1 m² regarding the technology of manual priming. With mechanized application, the specific consumption will increase by 10-15%.
to contents ↑Specific consumption of different primers
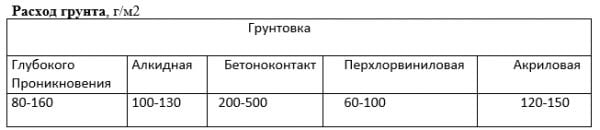
The consumption rate when working with alkyd primer compositions is 60-100 g / m². For old wooden surfaces of facades, maximum specific consumption data is accepted.
The most popular is a deep penetration primer.It is much more economical than alkyd compositions and is not critical to the initial characteristics of the internal coatings: their porosity, thickness, the presence / absence of plaster and other aspects.

Primer consumption of deep penetration ranges from 75-180 g / m². Such a significant spread is explained by the type of material to be primed. Maximum values correspond to brick, wood, bituminous mastics, plaster. The minimum flow rate is typical for metals that have previously been cleaned of rust, dirt (for example, when processing various pipes, finned surfaces of heating radiators). The consumption rate when working with an epoxy primer in these cases is much less - up to 100 g / m².
Primer consumption concrete contact has its own characteristics. Such compositions are designed for processing internal surfaces with low initial porosity, as well as with high roughness (for example, coated with quartz plaster). Since such a primer dries quickly, its specific consumption increases.
Another reason for the increased quantity is the need to create high-quality adhesion of the treated surface to paint, bitumen mastic or tile glue. Therefore, acceptable values for concrete contact primers are considered norms of 250-400 g / m².





