In many old buildings you can see parquet floors, whose age is several hundred years. If such coatings were subjected to cycling once every several decades, the parquet would have worn out long ago. The secret to the preservation of old floors is parquet oil. Oil-lubricated wood is a real alternative to varnishing.
- Advantages and disadvantages
- When to prefer oil
- The mechanism of action of oil
- Types of parquet oils
- Chemical composition
- Color schemes
- Product concentration
- Wear resistance
- Wet Compositions
- Flooring oil
- Cold way
- Hot way
- Floor care
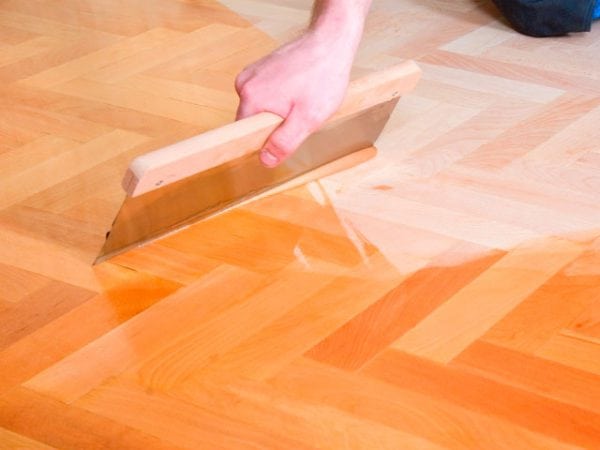


Advantages and disadvantages
Oiling wood has several significant advantages over varnishing.
- impregnation works are carried out more quickly than in the case of varnishing;
- the oiled floor is more resistant to moisture (for example: the decks of ships were previously treated with oil);
- the floor treated with impregnation can be restored in parts, while in the case of a varnished surface this is not possible;
- wood “breathes”, which positively affects its appearance and useful life;
- the total cost of repairs is lower than in the case of varnish.
Oil-treated floors and flaws are not without:
- restoration work should be carried out regularly - every 2-3 years;
- at first, such a floor is more polluted than varnished.
When to prefer oil
Oil formulations should be used in the following cases:
- the wood species itself contains a significant proportion of natural oils;
- the material from which the parquet is made is sensitive to temperature fluctuations and humidity (for example, beech);
- under the parquet there is a “warm floor” system;
- parquet is located outside the premises (for example, on the terrace);
- There is regular contact with water (for example, near a reservoir or in a bathroom).
Oiled floors are much nicer than varnished, if you walk barefoot on them - such surfaces are more natural. Varnish conceals the structure of the tree, its bumps. Impregnation leaves everything as it is.

The mechanism of action of oil
Paintwork material creates a thick membrane on the treated surface. The membrane provides a certain grip on the floor. Unlike varnish, oil impregnates wood, penetrating into the pores of the material. But on the surface there is a small amount of oil. Although no protective film is created, wood gains the necessary strength.
Compared to varnishing, oil treatment is preferable. The fact is that any wooden structure exchanges moisture with the environment. Both varnish and oil are approximately equally resistant to moisture reception - neither one nor the other composition can fully replace waterproofing, but can only provide some level of protection against moisture. A completely different situation with the return of moisture: the oiled material easily gives it away, but the varnish film prevents the departure of moisture. As a result, both wood and the lacquer membrane suffer - gradually they become worthless.
The decision to apply impregnation to the parquet requires a responsible approach, since if the oil is oiled, then in the future it will not work to cover the floor with varnish. If the old layer of varnish can be cycled and sanded, the oil leaves a much deeper mark - it penetrates the internal structure of the tree. As a result, even very thorough cycling will not give the desired effect, since many wood species are very responsive to oiling.
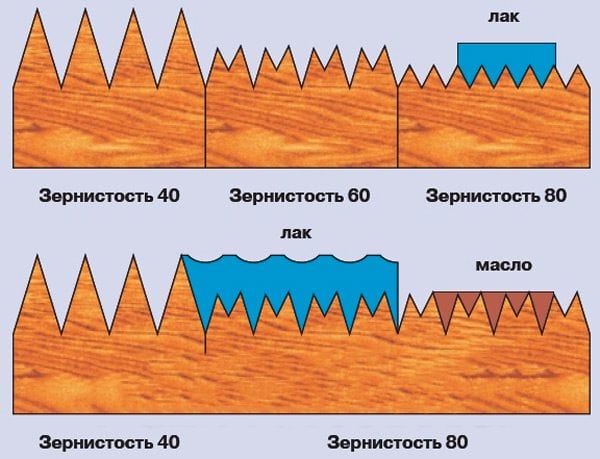
To switch from oil to varnish, you can apply a primer in several layers - this will block the exit of oil. However, in reality, such actions may not give the desired result, since the varnish effect will soon begin to peel off, especially with a mechanical load on the coating.
to contents ↑Types of parquet oils
Oils can be classified according to several criteria.
Chemical composition
Impregnation for processing parquet can be of natural or artificial origin. Natural products can be based on mineral or plant components.
Wax can increase the effectiveness of oiling. In many compositions, it is included initially. When wax is absent as an integral component, it must be used additionally. If we are talking about an artificial product with the addition of polyurethane, wax is not necessary.
All solutions contain solvents (e.g. White Spirit). Therefore, the environmental friendliness of impregnation is a relative issue. Some manufacturers add dearomatized gasoline, which does not give an unpleasant odor, as a solvent.
to contents ↑Note! The Blue Angel icon indicates the ability to use the product in places where children are constantly present.
Color schemes
Pigment can be added to the oil to obtain the desired shades. If it is not in the original composition, the pigment can be purchased separately. The higher the pigment component (usually its proportion is 7-10%), the more saturated and darker the floors will be. At the same time, the decorative effect is noticeable right there - you do not need to wait for it.
Different varieties of oils give different levels of gloss. This indicator is measured in%. Usually, the oil gives a semi-matt shade, although there are compounds that form a glossy shine. Moreover, glossy parquet, despite its visual appeal, is more difficult to maintain. In addition, even small defects are clearly visible on the glossy surface.
There are not only colorless, but also colored varieties of oils (for example, white). Unlike paint, colored oil does not hide the natural structure of wood.

Product concentration
Impregnations are carried out in various concentrations, depending on the amount of added solvent.
- thick impregnations - from 80 to 90% of the natural component;
- medium viscosity impregnations - the proportion of the natural component is in the region of 50%;
- liquid impregnations, where the proportion of solvent reaches 60-75%.
The density of the composition directly affects the number of oil layers required. Moreover, thicker impregnations are worse absorbed into the wood. But products with a significant proportion of solvent penetrate the wood much better. To obtain a balanced result, the compositions are combined (especially if the oil is applied for the first time): first, impregnation with a large proportion of solvent (as a primer) is used, and they are finished with a thick solution.
to contents ↑In the future, for surface care, you will need periodic treatment of the parquet with liquid impregnation. The solution penetrates deep into the wood, as a result of which the composition is updated and its protective capabilities are maintained.
Wear resistance
The wear resistance of the impregnation is differentiated by the degree of load on the parquet. There are compositions for heavy workload (parquet is processed in corridors, living rooms, kitchens), as well as for light workloads (used in bedrooms and other places with not very heavy traffic). Heavy duty oils are in a higher price category.
Wet Compositions
This is a separate category of impregnation, used for processing floors in showers, saunas, and bathrooms. The use of a specific composition is related to the standard temperature conditions in the room. If it is characterized by high temperature, only natural oil is used. For bathrooms, compositions with the addition of antiseptics are used.
Oils are also classified according to the place of application: outside or inside the building. If the wood flooring is located on the terrace, it is necessary to use impregnation specially designed for such conditions.

Flooring oil
First of all, you need to prepare the floor - to grind it with a looping or grinding machine. Then you need to remove all the dust.
The impregnation is well mixed in a container (this applies especially to color compositions). A wide brush with a long pile is optimal for surface treatment. The average consumption of the solution is a liter per two dozen square meters.
The oil composition can be applied in two ways: cold or hot.
to contents ↑Cold way
The impregnating composition is applied in a good layer on the floor. Rubbing it is not necessary. After 15-20 minutes, the wood will take all the oil that it can take. The remainder of the solution is removed with a cloth from the cotton fabric. Then you should treat the parquet with a polishing machine and wipe the floor again.
The second layer is applied to the surface after drying of the first, but not earlier than 5-12 hours (specific parameters are indicated on the bank). Before applying the second layer, you need to make the surface matte by treating it with a 230 grit sandpaper. The principle of applying the second layer is the same as the first, only the oil consumption will be significantly reduced, since the floor already contains a fair amount of it.
The final crystallization of the surface is completed within 3-14 days. At the same time, it is important to wipe the surface well after applying the oil, as well as observe the temperature regime (ideally around 20 degrees heat).
to contents ↑Note! A well-crafted floor is slightly shiny. This shine is often called "satin."
Hot way
Hot composition is better absorbed by wood. The solution is heated to 80 degrees in a water bath and then put with a spatula on the parquet.
Important! Before processing, the parquet must be heated with a thermal drop - this is how oil is absorbed better.The second layer is applied after 2-3 hours. With a hot technique, the surface should turn out without matte stains.
If you need to make a wax coating, you can start work no earlier than 2 days after applying the last oil layer. Re-polishing with hard wax is allowed after 3 hours or later.

Floor care
The first 7-10 days, you need to carry out regular cleaning with a broom vacuum cleaner or a dry rag. Floors can be cleaned with soapy water or special cleaning products for oiled parquet. To gain shine, the parquet is periodically lubricated with solid wax or mastic.
Applying oil to the flooring is a fairly simple process. All work can be done independently. You just need to be careful and follow the instructions.



