The word "polymer" immediately suggests thoughts on modern material - plastic, which is widely used in construction, repair, and everyday life. Polymeric substances are part of paints, building mixtures, putties.
- What is polymer plaster
- Types of polymer plaster
- Acrylic plaster
- Silicone plaster
- Silicate Plaster
- Siloxane plaster
- Cement plaster
- Polymer decorative plaster
- Scope and properties
- Application technology
- Surface preparation
- Solution preparation
- Instruments
- Plastering
- Manufacturers

Professionals often replace classic cement mortar with a material such as polymer plaster, because it is characterized by higher strength and durability and has many other advantages.

What is polymer plaster
The main difference between polymer plaster mixes and mineral mixes is that instead of inorganic binders they are based on dispersions of resins (acrylic, urethane and others). It is impossible to make such plasters with your own hands directly at the construction site, since to ensure proper properties plasticizers, modifiers, special fillers are introduced into their composition in strictly calibrated proportions. Therefore, each polymer material is sold in finished or dry form in factory packaging.
Depending on the type of solvent, polymer plasters can be used in different conditions. Many compounds are diluted with water, that is, their basis is water dispersion. Such tools are intended for internal use or are universal. Plasters on organic and other solvents are applied only on street surfaces and are intended primarily for facade work.

Types of polymer plaster
Each synthetic plaster in the base contains polymer components that determine its properties. According to the classification by composition, acrylic, silicone, silicate, siloxane and some other types of plasters are found.
Acrylic plaster
This material has the highest popularity among polymer plasters. Acrylic building mixture consists of polyacrylic resins with the addition of fillers, dyes, modifying components. After application, water evaporates, the polymerization of resins occurs with the formation of a durable, moisture-resistant, but vapor-permeable structure. Simply put, a hardened layer of acrylic plaster is not afraid of water, but partially passes gases, so it does not violate the microclimate in the room and does not cause dampness on the walls.
Acrylic plaster has other advantages:
- easily connects to concrete and other mineral substrates;
- suitable for interior and exterior decoration, most often contains frost-resistant additives;
- does not deteriorate from exposure to ultraviolet radiation, almost does not fade in the sun;
- includes substances that increase fire resistance;
- makes it possible to wash off the unsuccessfully applied area with water and perform a new layer;
- has sufficient elasticity, so it does not crack from vibration, displacements of the base.

Acrylic plasters also have a number of negative properties. So, if the porous base is not primed, moisture from the plaster will be drawn even before the polymerisation of the resin, which will disrupt the natural drying process. It is advisable to use primers with deep penetration, and apply at least 2 layers (we are talking about concrete and brick surfaces).
Acrylic resins themselves are combustible, therefore manufacturers introduce special additives to the composition of plasters that reduce the risk of fire. However, it is not recommended to apply mixtures on surfaces near an open flame. The dried layer of acrylic plaster attracts a lot of dust due to the tendency to strong static, and you will have to do cleaning more often. Another negative quality is associated with the need to apply the material without long interruptions in work. Otherwise, ugly borders will appear between the individual sections.
to contents ↑Silicone plaster
The composition of this material includes silicone resins, modifiers, emulsifiers, as well as structural fillers - stone chips, mineral flour, silica sand and others. The cost of silicone mixtures is an order of magnitude higher than the price of acrylic, but the quality is also at the highest level.
Silicone plasters are highly flexible. The coating formed by them can seriously stretch, so it does not crack even with significant shrinkage of structures or shifts that are characteristic of earthquake-prone zones. Silicone mixtures have many other positive qualities:
- universal in application - suitable for the street and internal works;
- frost-resistant, weather-resistant, withstand the regular effects of precipitation, wind;
- serve for decades without loss of aesthetic properties;
- have high vapor permeability, while literally repel water, create a waterproofing coating on the surface;
- They boast excellent adhesion to a wide variety of building materials;
- UV resistant, do not fade, their color does not fade;
- do not have restrictions on the thickness of the finishing layer (still more often act as a thin-layer coating due to the high cost);
- withstand heat and temperature changes, do not soften after complete polymerization;
- durable, do not respond to moderate mechanical stress;
- strengthen weak bases, extend the term of their maintenance-free service.

Silicate Plaster
The basis of such plaster is molten (liquid) glass. May include mineral fillers, tinting agents, plasticizers, modifiers. Typically, silicate plasters are used for outdoor work, because they have increased resistance to damage, abrasion, wear. They are incredibly resistant to temperature extremes, any precipitation and wind, aggressive operating conditions.
Often silicate mixtures are used to warm rooms, because they have excellent thermal insulation abilities, and also enhance sound insulation. The plasters are waterproof, but allow air and moisture to pass through, therefore they are suitable for all rooms without restrictions. The minimum service life of the finished layer is 20 years. The adhesion of silicate mixtures with concrete, brick, any insulation is considered maximum. They are not subject to dust and pollution, do not support combustion, are fireproof, dirt is easily washed off from them.
Among the minuses of such funds are worth noting:
- short shelf life of the finished mixture, the complexity of application for beginners;
- medium elasticity;
- meager colors;
- high price;
- tendency to fade color.
Silicate plasters are made not only in finished form, but also in the form of a dry building mixture, so you can choose a convenient option in terms of volume and cost.
to contents ↑Siloxane plaster
Siloxane in chemical structure resembles silicone, representing its "immature" version.It is the siloxane molecules that, after combining, become silicone. Most siloxane plasters additionally contain acrylic, and in greater quantities. In fact, acrylic plays a dominant role in such building mixtures, and siloxane is designed to form a thin waterproof film on the surface of the plaster layer.
Siloxane plasters are cheaper than silicone plasters, but do not provide moisture protection throughout their entire thickness. With external use, surface waterproofing is gradually destroyed under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, and the moisture resistance of the coating drops sharply. Due to the short service life, materials based on siloxane should be used only indoors, or regularly update the finish.

Cement plaster
It is known that strong and reliable cement plasters have a number of significant disadvantages. The disadvantages of such building mixtures are weak extensibility, susceptibility to cracking from shrinkage and vibration of buildings. To level them, a polymer-cement plaster was developed, which is a mixture based on cement and at least 30% polymer fibers. The following indicators seriously increase in such material:
- tensile strength, bending;
- resistance to abrasion, cracking;
- adhesion to building materials;
- plasticity and elasticity;
- workability;
- heat resistance.
to contents ↑Polymer-cement plasters can be applied with a fairly thin layer while maintaining the operational and protective properties of the coating. They cover cracks, joints, pits and seams, and are used for restoration work. Mixtures are made only in dry form, because the cement hardens quite quickly after contact with water. The price of the compositions is lower than that of other polymer plasters, so this finish option is considered economical.
Polymer decorative plaster
A variety of polymer building mixtures are considered decorative, which, in addition to the base, contain a structural filler or are pigmented. The following additives can act as a filler:
- pebbles, ground stone or stone flour;
- different types of sand;
- expanded clay and vermiculite;
- artificial fibers;
- shells or fragments thereof;
- mica;
- metal dust;
- flocks.
Decorative polymer plaster may be finely dispersed or contain inclusions of a larger fraction. The aesthetic effect is created due to the coloring of the plaster, the interesting form of the filler, the special techniques of finishing the layer. The material may be uniform in texture or contain inclusions of different sizes (small and part of larger ones). Examples of possible polymer stucco textures are:
- roughness, or the effect of "goosebumps" (obtained from fine-grained plaster);
- relief (created by roller, brush, notched trowel);
- "Bark beetle" (formed by grinding a mixture with large granules).
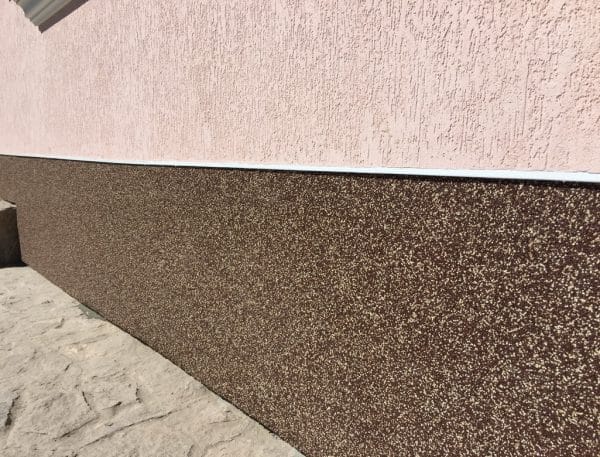
Scope and properties
Most building mixtures are considered universal, they can be used for work indoors and outdoors. However, some formulations have a more specific purpose - either for street or indoor use. On sale you can also find facade plasters and materials for building socles. Polymer building mixtures are suitable for finishing concrete, brick, wood, metal, drywall or previously plastered substrates.
The properties of polymeric materials are as follows:
- strength, impact resistance;
- wear resistance;
- elasticity;
- ductility during application;
- moisture resistance;
- vapor permeability;
- frost resistance;
- weather resistance;
- alkali resistance;
- environmental friendliness.
to contents ↑Polymer blends provide additional protection against noise, improve thermal insulation of buildings and structures. There are white (unpainted) compounds on sale, as well as already tinted plasters. It must be remembered that most polymer-based plasters are not used for roughing - they are applied with a sufficiently thin layer and cannot repair large cracks and other serious defects. Therefore, before starting work, you will have to align the base with the differences using the mineral composition.
Application technology
Working with polymer compositions is more like puttying, because the performed layer will be only a few millimeters. On the basis of minor defects that are no more than 3 times greater than the diameter of the grains of the filler. If the polymer material is applied too thick, irregularities will be very striking, as will the uneven color of the coating. The plastering process is carried out at an air temperature within + 5 ... + 30 degrees, humidity - less than 80%.
to contents ↑
Surface preparation
First, the old coating is removed, the base is cleaned of dirt, grease spots are rubbed with a solvent. Cracks are embroidered, sealed with a cement mixture, they are allowed to dry. The surface is primed to bind dust, strengthen the base, equalize absorbency and enhance adhesion.
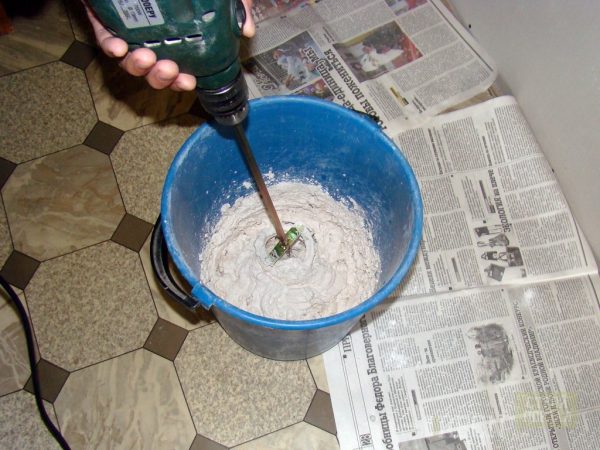
to contents ↑Solution preparation
Mix the prepared mixes well enough before applying directly in the factory packaging. Acrylic, silicate plasters with excessive thickening are diluted with water, but not more than 10%. Dry mixtures are diluted with liquid according to the instructions, accurately measuring the proportions and introducing the dry components into the water, and not vice versa. After the first kneading with a construction mixer, the solution is left for 10 minutes to “ripen”, then mixed again and taken to work. It is important that the mass has optimal density, otherwise it will creep off the wall or it is difficult to rub along the wall.
to contents ↑Instruments
Typically, a trowel (trowel), a spatula is used to apply the material, and a grater (polyurethane or metal) for leveling. You also need to pre-prepare a construction plummet, masking tape to close window and doorways, rags. If you plan to apply drawings, you must have on hand rollers, dies or stencils.

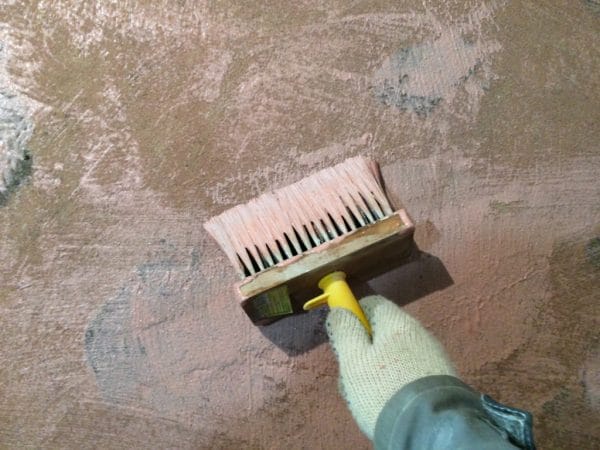
Plastering
The material is collected with a spatula, imposed on the surface of the wall. When leveling, hold the tool at an angle of 40-50 degrees, performing a thin layer. In addition to the spatula, it is convenient to apply the polymer mixture with a trowel, pulling it with an even layer. You can perform strokes from the bottom up or, conversely, from top to bottom. Work from corner to corner is carried out in one approach. If you have to take a break, masking tape is glued along the line of the last application of the solution, and after resuming plastering, remove it.
Within 15 minutes after applying the solution, take a grater and begin to mash or give a decorative texture. The plaster does not adhere to the tool, but is not yet solid. It is impossible to delay the mashing process, since a strong film is formed on the surface that can be damaged. The polymer mixture should dry within 24-48 hours, and at this time it must be protected from direct sunlight, drafts, temperature extremes.

Manufacturers
In the construction market, polymer plaster is represented by all well-known manufacturers - Baumit, Ceresit, Knauf, Weber, Bergauf and many others. Domestic compositions are usually much cheaper than imported ones. The most popular plasters are:
- Ceresit CT 60 Super - acrylic pebble;
- Ceresit CT 63 Super - acrylic "bark beetle";
- Ceresit CT 77 - acrylic mosaic;
- Caparol Streichputz - matte silicone;
- SilexColor Tonachino - silicate with the effect of an aged surface;
- "Bergauf Finish Polymer" - acrylic white.
Polymer plasters are considered the most high-quality and practical finishing material. They are distinguished by excellent operational properties, a long service life and attractiveness, which stand out against the background of other coatings.










