Among all existing types of destruction of metals, electrochemical corrosion, which occurs as a result of its interaction with an electrolytically conductive medium, is most often encountered. The main reason for this phenomenon is the thermodynamic instability of metals in the environments that surround them.
- Main varieties
- Intergranular
- Pitting
- Crevice
- How is different types of corrosion manifested?
- Rust Protection Methods
- Method number 1
- Method number 2
- Method number 3
- Method number 4

Many objects and structures are subject to this type of corrosion:
- gas and water pipelines;
- elements of vehicles;
- other constructions made of metal.
Corrosion processes, that is, rust, can occur in the atmosphere, in the ground, and even in salt water. Cleaning metal structures from manifestations of electrochemical corrosion is a complex and lengthy process, therefore, it is easier to prevent its occurrence.
to contents ↑Main varieties
When corrosion occurs in electrolytes, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. In this regard, it is called electrochemical. It is customary to distinguish the following types of electrochemical corrosion.
Intergranular
By intergranular corrosion is meant such a dangerous phenomenon in which the grain boundaries of nickel, aluminum and other metals are destroyed selectively. As a result, the strength and plastic properties of the material are lost. The main danger of this kind of corrosion is that it is not always visually noticeable.
Pitting
Pitting electrochemical corrosion is a point lesion of individual sections of the surface of copper and other metals. Depending on the nature of the lesion, there are closed, open, as well as surface pitting. The size of the affected areas can vary from 0.1 mm to 1.5 mm.
Crevice
Crevice electrochemical corrosion is usually called the enhanced process of destruction of metal structures at the locations of cracks, gaps and cracks. Crevice corrosion can occur in air, gas mixtures, and sea water. This type of destruction is characteristic of gas pipelines, the bottoms of ships and many other objects.
Corrosion is common under conditions of a small amount of oxidizing agent due to a difficult approach to the walls of the gap. This leads to the accumulation of corrosive products within the gaps. The electrolyte contained in the internal space of the gap may change due to the hydrolysis of corrosion products.
In order to protect metals from crevice corrosion, it is customary to apply several methods:
- sealing of gaps and crevices;
- electrochemical protection;
- inhibition process.
As prophylactic methods, only those materials that are least susceptible to rust should be used, as well as the competent and rational construction of gas pipelines and other important objects from the very beginning.
Proper prevention in many cases is a simpler process than subsequent cleaning of metal structures from stubborn rust.
to contents ↑How is different types of corrosion manifested?
As an example of the course of the corrosion process, we can cite the destruction of various devices, car components, as well as any structures made of metal and located:
- in the air;
- in waters - seas, rivers contained in the soil and under the soil;
- in technical environments, etc.
In the process of rusting, the metal becomes a multi-electronic galvanic cell. So, for example, if copper and iron come into contact in an electrolytic medium, copper is the cathode, and iron is the anode. Giving away the electrons of copper, iron in the form of ions enters the solution. Hydrogen ions begin to move towards copper and are discharged there. Becoming more and more negative, the cathode soon becomes equal to the potential of the anode, as a result of which the corrosion process begins to slow down.
Different types of corrosion manifest themselves in different ways. More intensively, electrochemical corrosion manifests itself in those cases when there are inclusions of metal with less activity in the cathode compared to corroding - rust appears on them faster and is quite expressive.
The occurrence of atmospheric corrosion occurs in humid air and normal temperature. In this case, a film of moisture with dissolved oxygen is formed on the metal surface. The process of metal destruction becomes more intense with increasing air humidity and the content of gaseous oxides of carbon and sulfur, provided that:
- cracks;
- roughness;
- other factors that facilitate the condensation process.
Soil corrosion most affects a variety of underground structures, gas pipelines, cables and other structures. The destruction of copper and other metals occurs due to their close contact with soil moisture, which also contains dissolved oxygen. The destruction of pipelines can occur six months after the date of their construction if the soil in which they are installed is characterized by increased acidity.
Under the influence of stray currents emanating from foreign objects, electrical corrosion occurs. Its main sources are electric railways, power lines, as well as special installations operating on a constant electric current. To a greater extent, this type of corrosion provokes the destruction of:
- gas pipelines;
- all kinds of structures (bridges, hangars);
- power cables;
- oil pipelines.
The action of the current provokes the appearance of sections of the entrance and exit of electrons - that is, cathodes and anodes. The most intense destructive process is precisely in areas with anodes, so rust is more noticeable on them.
Corrosion of individual components of gas pipelines and water pipelines can be caused by the fact that the process of their installation is mixed, that is, occurs using various materials. The most common examples are pitting corrosion occurring in copper elements, as well as bimetal corrosion.
In the mixed installation of iron elements with copper and zinc alloys, the corrosion process is less critical than in copper casting, that is, with copper, zinc and tin alloys. Pipeline corrosion can be prevented using special methods.
Rust Protection Methods
Various methods are used to combat insidious rust. Consider those that are most effective.
Method number 1
One of the most popular methods is the electrochemical protection of cast iron, steel, titanium, copper and other metals. What is it based on?
Electrochemical processing of metals is a special method aimed at changing the shape, size and surface roughness by anodic dissolution in an electrolyte under the influence of electric current.
In order to provide reliable protection against rust, it is necessary to treat them with special means even before starting to use metal products, which in their composition contain various components of organic and inorganic origin.This method allows you to prevent the appearance of rust at a certain time, but later you will have to update the coating.
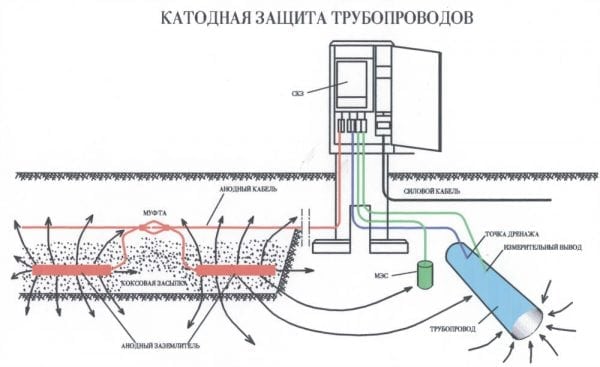
Electrical protection is a process in which a metal structure is connected to an external source of constant electric current. As a result of this, a polarization of cathode type electrodes is formed on its surface, and all anode regions begin to transform into cathode ones.
Electrochemical processing of metals can occur with the participation of the anode or cathode. In some cases, alternating processing of the metal product with both electrodes occurs.
Cathodic corrosion protection is necessary in situations where the metal to be protected does not have a predisposition to passivation. An external current source, a special cathodic protection station, is connected to a metal product. This method is suitable for protecting gas pipelines, as well as water and heating pipelines. However, this method has certain drawbacks in the form of cracking and destruction of protective coatings - this occurs in cases of a significant displacement of the potential of the object in the negative direction.
to contents ↑Method number 2
Electrospark processing of metals can be carried out using plants of various types - non-contact, contact, as well as anode-mechanical.
Method number 3
To reliably protect gas pipelines and other pipelines from rust, a method such as electric arc spraying is often used. The advantages of this method are obvious:
- significant thickness of the protective layer;
- high level of performance and reliability;
- the use of relatively inexpensive equipment;
- simple technological process;
- the possibility of using automated lines;
- low energy costs.
Among the disadvantages of this method is the low efficiency in the processing of structures in corrosive environments, as well as insufficient adhesion to a steel base in some cases. In any other situations, such electrical protection is very effective.
to contents ↑Method number 4
To protect a variety of metal structures - gas pipelines, bridge structures, all kinds of pipelines - effective anti-corrosion treatment is required.
This procedure is carried out in several stages:
- thorough removal of body fat and oils using effective solvents;
- cleaning of the treated surface from salts soluble in water - is carried out using professional high-pressure apparatuses;
- removal of existing structural errors, edge alignment - this is necessary to prevent chips from the applied paintwork;
- thorough surface cleaning with a sandblasting apparatus - this is done not only to remove rust, but also to give the desired degree of roughness;
- application of anticorrosive material and an additional protective layer.
Proper pre-treatment of gas pipelines and all kinds of metal structures will provide them with reliable protection against electrochemical corrosion during operation.











