Welds are responsible for the integrity of the metal structure. In particular, the connection should be strong enough, resistant to rust, moisture. Weld processing is designed to meet these challenges.
- Processing methods
- Heat treatment
- Heat treatment equipment
- Heat Treatment Methods
- Mechanical restoration
- Chemical treatment

Processing methods
There are three methods by which welded joints are protected:
- Heat treatment. Thanks to this method, it is possible to remove residual stresses in the material arising from welding operations. Heat treatment is carried out according to one of two technologies: local, when only the connection itself is warmed up or cooled, or general - the entire part is subject to heat treatment.
- Mechanical restoration. In this case, the task is to remove residual slag and verify the reliability of the connection. A typical example of machining is tapping a seam with a hammer or stripping it. If the slag is not removed, corrosion may develop.
- Chemical treatment. The application of protective coatings to the compound is one of the ways to deal with corrosion processes. The most affordable chemical protection option is the treatment of the seam with a primer and varnish-and-paint material.
Below we dwell on weld protection technologies in more detail.
to contents ↑Heat treatment
In addition to reducing the residual stresses of the metal, heat treatment allows you to achieve the following goals:
- to make the structure of the seam and heat-affected zones more adapted to the influence of external factors;
- optimize the physical and operational properties of the material, in particular, increase resistance to rust, heat resistance, etc.
Heat treatment of welded joints involves heating for a certain time the welded joint or all the metal to a given temperature. Next, there is artificial cooling, which is also performed according to a specific scenario.
to contents ↑Heat treatment equipment
Four types of technological equipment can be used for heat treatment of joints:
- Induction devices. Induction heating is often used during piping. The essence of this method is the use of copper inductors, including multicore copper cable with air cooling. When mounting the inductor in the pipe, the distance between the pipe and the inductor must be taken into account. General rule: the greater the gap between the objects, the worse the power of the equipment is used.
- Flexible resistance heaters. This method is considered one of the most convenient and affordable methods for processing welds.
- Muffle furnaces. When working with this type of equipment, special attention should be paid to the uniformity of heating of the joint, which is achieved by the off-center installation of the part in the furnace.
- Heating with gas equipment. When gas-flame heating, welding and special multi-flame gas burners are used. Gas heaters emit thermal energy resulting from the combustion of a mixture of combustible gas with oxygen.
Equipment for heating is selected based on the installation conditions, the availability of one or another type of device and other circumstances.Heating equipment must meet certain requirements: clearly dock with welds, have a mass not too large and ensure uniform heating of the joint both in width and in length.
To reduce heat loss, all kinds of heat insulators are used in the heat treatment of welded joints.
Thermal insulation should be heat-resistant with low thermal conductivity, strong, but at the same time flexible, resistant to wear and safe in operation.
to contents ↑Heat Treatment Methods
Several methods for heat treatment of welded joints are known:
- Preheating. It is used both before welding and at the time of welding parts. This type of heat treatment is used in welding structures of low carbon steel. Metal warms up to 150-200 degrees Celsius.
- High vacation. The technique consists in heating the material to 650-750 degrees Celsius (the specific temperature indicator depends on the grade of steel). The temperature is maintained for 5 hours. The technology allows to reduce stress by 80%, as well as to increase the resistance of the material to mechanical stress and increase its elasticity.
- Normalization. Applied to carbon and low alloy steel grades. A similar heat treatment of the compound is carried out at temperatures from 950 degrees Celsius. At the end of heating, exposure and cooling are performed under ambient conditions. Normalization makes it possible to reduce the graininess of the metal, reduce stress, and also increases the strength of the seam.
- Austenization. It is a hardening of the welded joint by heating it to a temperature of 1070 degrees and above. The part is heated for 60 minutes, and then quick artificial cooling is performed. The technique is widely used for quenching austenitic steels. The result of austenization is the increased elasticity of the welded joint.
- Stabilization. Stabilizing annealing differs from austenization by a lower temperature and a shorter metal exposure time.
- Thermal rest. The technology consists in heating the weld to 250-300 degrees Celsius. Then the metal is held in a preheated state. As a result of the procedure, the level of diffuse hydrogen in the welded joint is reduced, and internal stresses are reduced.
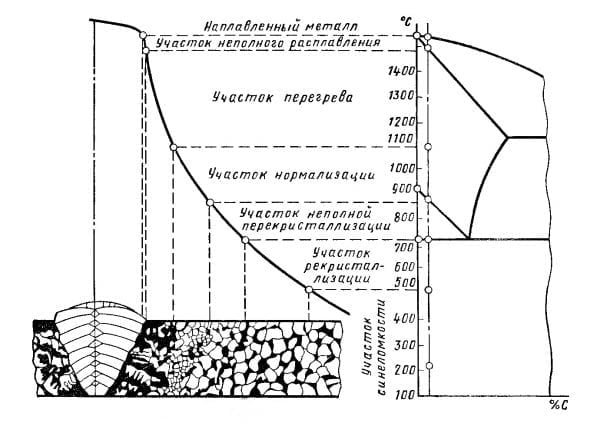
The choice of the method by which the heat treatment of welded joints will be carried out depends on the physicochemical characteristics of the steel (determined by its grade). Of particular importance is the fulfillment of technological requirements, otherwise, there is a deterioration in the quality of the welded joint.
Key parameters to consider when conducting local heat treatment:
- width of the heated section;
- uniformity of heating along the wall thickness and the width of the heated section;
- holding period;
- cooling rate.
Mechanical restoration
The mechanical elimination of welding imperfections is carried out using a wire brush. You can greatly simplify the task and make cleaning better if you use a portable grinding device or grinder with a petal nozzle. Instead of a nozzle, an abrasive wheel can also be used.
Mechanical cleaning allows you to remove the following defects of the welded joint:
- scale;
- burrs;
- oxides;
- consequences of the rush.
Despite the simplicity and cheapness of the technology, there are a number of nuances regarding the choice of nozzles, the knowledge of which will allow us to perform better work:
- First of all, you need to choose a grinding wheel from a suitable material.An aluminum zirconate wheel is best suited for mechanical cleaning. The advantage of this material is that, firstly, it provokes corrosion processes, and secondly, aluminum zirconate is stronger than aluminum oxide, from which some types of nozzles are also made.
- The grinding wheel petals must be on the fabric component. The fabric is more reliable and more resistant to heavy loads in comparison with paper, which is sometimes used on the petals as the basis. However, such nozzles cost much more analogues on a paper basis. The higher cost of fabric nozzles is justified and will pay off with such aggressive work with respect to the material as grinding joints.
- The size of the abrasive grain depends on the type of work performed. Very often, when cleaning compounds, nozzles with different grain sizes may be needed. Therefore, it is recommended to purchase several types of nozzles at once.
- If you need to qualitatively clean the seam, then different grain sizes are simply necessary, since grinding is carried out with a gradual change of nozzles for smaller grains. For example, large scale is removed by coarse nozzles, but fine grinding is done by fine-grained nozzles. Finishing penetration is carried out by the finest grain. Nozzles should be changed sequentially - no more than one size pass is allowed. However, when it comes to creating a mirror-like sheen of a welded joint, not a single size should be missed.
- For processing joints located in hard-to-reach places (cavities, edges, holes), special devices are used - burrs installed in the grinder. There are a wide range of boring cutters of various sizes and shapes, so choosing the right configuration is not difficult.
Chemical treatment
The best results when processing welded joints are achieved with a combination of mechanical and chemical means. Two methods of working with seams are used: etching and passivation.
Etching is carried out before mechanical grinding. To carry out this operation, chemical compositions are used that provide a uniform coating that prevents corrosive processes. In addition, etching allows you to eliminate places affected by runaway. The fact is that in such places there is an accumulation of nickel and chromium oxides, as a result of which the steel is rusted.
On small areas of welded joints, it is recommended to etch by direct application of the composition to the surface to be treated. If the part is large enough or has a complex configuration, it should be placed in a container with an etching solution. The residence time of the metal in the etching flow is calculated individually in each situation.
When etching is completed, it is the turn of passivation. The process is the application of a special composition to a metal, as a result of which a film is formed. This protective coating prevents corrosion. From a chemical point of view, passivation can be explained as follows: oxidants, interacting with steel, remove free metal from the surface, while activating the formation of a protective film.
The chemical treatment is completed by cleaning the welded joints from the reagents. Rinse off water contains many toxic substances, heavy metals and acids. Acids are neutralized with alkalis, and then the remaining liquid is filtered. Disposal must be done only in specially designated areas in accordance with environmental legislation.







