Gum turpentine was known to people from antiquity. For example, in Egypt, he was part of a solution for mummification. Previously, it was extracted by steam distillation of coniferous resin, but now it is more often done by extraction or distillation methods, taking various parts of pine, fir and other coniferous trees as raw materials. Turpentine is widely used in medicine and a number of industries.
- Obtaining and types of turpentine
- Turpentine Composition
- Turpentine Properties
- Table of physico-chemical parameters of turpentine from turpentine oil
- Use of funds
- Toxicity and safety measures
- Where turpentine is sold, the price of the material

Obtaining and types of turpentine
Under turpentine is understood a product from resin of coniferous wood (gum), which is a liquid mixture of terpenes and terpenoids. It differs from essential oil by lower quality distillation and filtration, therefore without additional purification it is considered a substance that has exclusively technical purpose.
The production method and type of raw materials determine the kind of turpentine that will be obtained:
- Gum (turpentine oil). It is created by distillation of natural resin of pine or fir. After incision of the tree bark, a watery resin (gum) is released, which is then heated with steam, separating the prepared turpentine and the solid residue — rosin.
- Dry distillation (wood). It is obtained by dry distillation of parts of a tree that contain a lot of resin (for example, stumps).
- Extractional. It is produced by distillation of volatile fractions from resinous substances with the addition of organic solvents. Coniferous wood chips are usually taken as raw materials.
- Sulphate. It is a by-product in the production of cellulose from conifers by a special sulfate method (fractional distillation with wood chips digestion in caustic and sodium sulfide with the introduction of sodium sulfate). A toxic substance that does not dissolve in water, but is diluted with solvents.
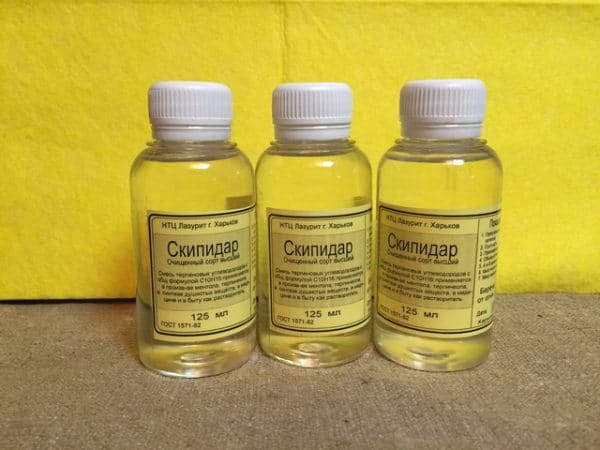
to contents ↑The safest for humans is natural gum turpentine, which is sold in pharmacies and used for medical purposes.
Turpentine Composition
Gum turpentine is an oily liquid with a pleasant spruce aroma. The main components of it are monoterpenes alpha-pinene, beta-pinene, also there are other terpenoids - myrcene, caryophyllene, dipentene and others, but to a lesser extent. The exact composition and percentage of these substances varies depending on the type of coniferous plant that has become the raw material for the production of resin, as well as the type of raw material: branches, wood chips, stumps, needles, etc.
to contents ↑Turpentine Properties
A whitish, slightly oily liquid with a coniferous smell is difficult to confuse with other substances. It is quite thick, but mobile, has a burning taste. The color of the product may be slightly whitish, yellowish, but not too saturated. Sulphate turpentine is able to dissolve fats, oils, resins, rubber. During the reaction with oxygen, it becomes more dense in shade, yellow.The tool changes its chemical composition when interacting with halogens, acids, ozone, oxides.
to contents ↑Table of physico-chemical parameters of turpentine from turpentine oil
According to GOST 1571-82, gum turpentine has a grade (top, first and second grades), depending on why its technical characteristics change. A common requirement is the appearance: any turpentine is a translucent volatile liquid with a specific odor that does not have water and sediment. The remaining data are given in the table:
| Indicator | Top grade | First grade | Second grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density at a temperature of +20 degrees, g / cu. cm | 0,855-0,863 | 0,855-0,863 | 0,855-0,863 |
| Refractive index | 1,465-1,472 | 1,465-1,472 | 1,465-1,475 |
| The volume fraction of distillation at a pressure of 760 mm RT. Art., temperature up to +170 degrees,% | 92 | 90 | 80 |
| Acid number per 1 g, mg KOH | 0,5 | 0,5 | 1 |
| The share of non-volatile residue,% | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,9 |
| The proportion of alpha, beta pinenes in the amount,% | 60 | 55 | 50 |
Use of funds
The areas of use of the product vary greatly depending on its type. For example, natural gum turpentine is widely used for medical purposes. It has a locally irritating, warming effect, causes blood flow to the diseased area of the body, therefore it is a component of balms, ointments for radiculitis, arthrosis.
Turpentine-based products also help from bruises, sprains. For cosmetic purposes, turpentine baths with special gum emulsions are used. In a number of countries, the product is used as a disinfectant, antiseptic, and a medicine for respiratory system diseases.
Sulphate, extraction turpentine - toxic products, but it also has a certain area of operation:
- dissolving paints, varnishes, making washes;
- production of camphor, boiled wax, shoe polish;
- release of a number of external veterinary drugs;
- removal of grease stains, degreasing of glass, plastic, plexiglass;
- manufacturing of insecticides, synthetic resins;
- production of household chemicals (after purification from harmful volatile substances).
to contents ↑
Toxicity and safety measures
Gum turpentine is a natural product, but its terpenes have strong sensitizing properties and cause allergies in some people (up to anaphylactic shock). With direct contact with the skin, it provokes irritation, redness, with eyes and mucous membranes - severe inflammation and chemical burns.
If you breathe in fumes, there is a risk of central nervous system damage with headache, weakness, apathy, impaired attention and memory. When penetrating through the mouth, the drug can lead to severe poisoning with a fatal outcome, especially in children! The cause of death is most often acute renal failure.
to contents ↑Sulphate turpentine is highly toxic, moreover, it is highly flammable. If it comes into contact with the skin, it causes a severe burn; its vapors lead to poisoning of the body and sharply irritate the mucous membranes. Like other organic solvents, the substance should be stored tightly closed, in a dark place, away from sources of heat and fire. Product residues are disposed of as special waste in special landfills.
Where turpentine is sold, the price of the material
Technical turpentine is sold in all construction, household, hardware stores. Its cost is from 400 rubles per liter and can be higher or lower depending on the container (in glass bottles of 200-500 ml, the product is much more expensive in terms of calculation than in barrels and canisters of 5-150 liters). Gum turpentine is sold in pharmacies (usually called “Terpentine Oil”), the price is 200-300 rubles per 100 ml.