Impregnated board is a special type of lumber, which is becoming increasingly popular in construction. There are not too many manufacturers of such impregnations, and the price is higher than that of ordinary wood. Impregnation of wood can seriously extend its service life and reliably protects from decay.
- Is there any harm from impregnation?
- Impregnation Details
- Impregnation Goals
- Impregnation depth
- Decay on cuts and inside
- Materials for processing
- Varieties of compositions
- For deep protection
- Weatherproof
- Antiseptics
- Flame retardants
- Combined formulations
- Deep impregnation methods
- Surface treatment
- Manufacturer's Suggestions

Is there any harm from impregnation?
Impregnation involves impregnation of wood with a special composition (Wolmanit CX-8, Tanaligh E 3494 and some others). As a result, rotting, mold damage, and other types of decomposition in the environment are prevented. For the treatment of natural wood, a special water-soluble preservative based on malachite and boric acid is most often used.

Due to the composition, the impregnating solution is not toxic, does not emit volatile substances. If earlier chromium and arsenic compounds were used to impregnate wood, then modern compounds are considered environmentally friendly and harmless to humans, animals, and the environment. That is why the impregnated tree is widely used for the cultivation of grapes, and in the Scandinavian countries it is generally everywhere in contact with land, water. After impregnation, the wood does not stain the skin, does not smell. The impregnations of this technology have all the necessary certificates and have been tested with respect to the impact on human health.
to contents ↑Impregnation Details
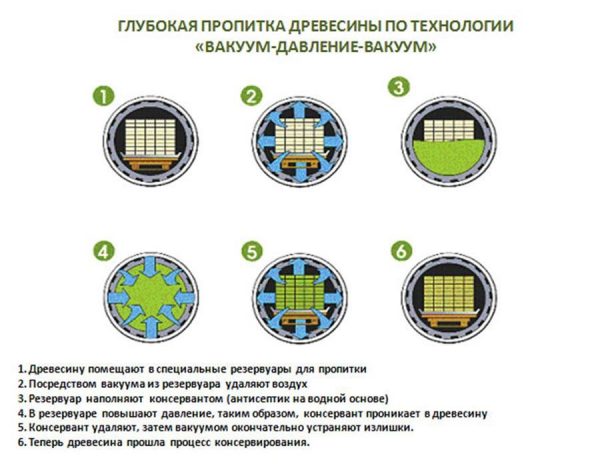
During impregnation, the wood is impregnated with an antiseptic, fungicidal, biocidal solution under pressure in hermetically sealed vacuum chambers. They contain pre-dried material, the fluid supply mode is controlled by a computer. After a certain period of time, the solution is removed from the chamber, after which the vacuum is again created until the tree completely dries. Finished products are immediately packaged and sent to sale.
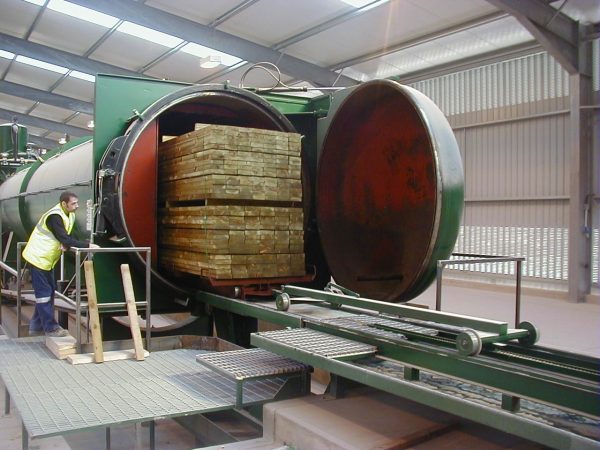

Impregnation significantly extends the life of the wood, making it virtually unlimited. The board will be moisture resistant, so it can be used to equip structures in the open air in any climate. The most popular impregnated wood products are:
- flower beds, benches, stairs;
- pavilions and arbors;
- fences, canopies;
- terraces, paths;
- sandboxes and playgrounds;
- moorings, bridges;
- exterior cladding of houses;
- load-bearing beams, balconies, attics;
- stakes, garters, columns for plants.
The solutions used to impregnate are called impregnates. They can act as preparations for deep or surface treatment, serve as a base soil. Most solutions are water based. Nevertheless, oil-based and organic solvent preparations are on sale, but they are not environmentally friendly.By means of this type, only technical wood is impregnated, which goes to the manufacture of telegraph poles, fences, sleepers for the railway.
Impregnation Goals
Specific fungi cause rotting of wood over time. Spores of these microorganisms are on any tree. They remain in a passive state until favorable conditions are created: the product enters a warm, humid place. The sapwood part of the wood, which becomes an excellent breeding ground for mushrooms, is most susceptible to decay. A dead, sound tree usually does not rot, since microorganisms cannot develop in it.
During impregnation, the porous wood structure is saturated with antiseptic substances that prevent or stop the reproduction of fungi, putrefactive and mold microbes, and other bacteria that lead to damage to the material. The use of impregnations, in addition to preventing rot, solves such problems:
- increased hydrophobicity;
- the exclusion of the population of the tree with pests;
- ensuring fire resistance;
- strength optimization;
- increase the service life of buildings.

to contents ↑After penetration, the impregnate fills the pores of the wood and makes it resistant to most adverse factors.
Impregnation depth
Impregnation is called the deep processing of wood with antiseptics, when its sapwood is impregnated with a solution of 95% (at least). Also captured to 0.2-0.5 cm of the core, which is adjacent to the sapwood.
The nuclear layer does not need to be processed, as it is subject to the so-called natural impregnation. There are phenols that have an antiseptic effect and prolong the life of the tree. Before impregnation begins, the material must be dried, otherwise moisture in the sap portion will interfere with the penetration of impregnation into the intercellular space.
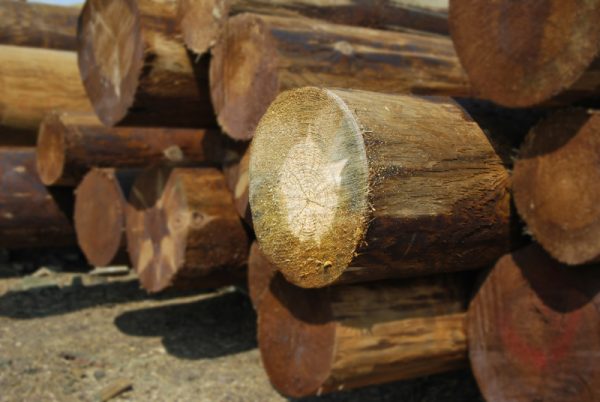

Decay on cuts and inside
With strict adherence to impregnation technology, rotting of the boards from the inside is excluded. The only risk is found when processing roundwood columns in which the sapwood is poorly dried. Due to the large thickness, the wood cannot be completely saturated, therefore, its lower layers theoretically remain rotten when in contact with the ground.
Rotting wood on saw cuts after impregnation is almost impossible. If you are supposed to constantly touch the ground, it is recommended to cover the contact surface with oil impregnation for additional protection. Another option is to apply end-face sealant to the saw to prevent destruction.

Materials for processing
Impregnation technology is applied to materials that are most often affected by damaging factors and prone to decay:
- floorboard;
- terrace, balcony;
- blanks for outdoor furniture;
- wood for arbors, canopies, attics;
- material for fences;
- timber.

Varieties of compositions
Depending on the components, the features of the action, all impregnates are divided into several groups.
For deep protection
Most of the compounds are designed specifically for deep impregnation of wood, which implies impregnation technology. Such solutions must be safe, environmentally friendly, not contain caustic, toxic components. These funds penetrate into the deep layers of the material, fill the pores, providing the most reliable and highest level of protection.
Weatherproof
Such solutions additionally enhance the strength of wood, which helps to increase its resistance to atmospheric factors. After drying, the tree will not be afraid:
- rain, snow, hail;
- temperature differences;
- climatic fluctuations;
- change of seasons;
- ultraviolet radiation;
- fogs;
- high humidity;
- continuous heating.

to contents ↑Without impregnation, the wood quickly deteriorates from the influence of such factors, and after processing with special compounds, the material will not crack, dry out and rot for many years.
Antiseptics
Almost all formulations contain antiseptic components (e.g. boric acid). They inhibit the reproduction of fungi, mold, bacteria, and also prevent the appearance of bark beetles, worms, other pests and parasites. Biocides not only prevent the development of putrefactive processes, but also stop the ongoing changes.

to contents ↑Coniferous wood requires special protection: such materials are destroyed quite quickly. Therefore, when building street structures and structures from spruce or pine boards, timber, other lumber, it is recommended to impregnate in advance.
Flame retardants
A dry tree supports combustion well, therefore it is practically defenseless in front of a fire. To reduce the spread of fire, reduce smoke generation, special components are included in the composition of the range of impregnations - flame retardants, which prevent fire and reduce the rate of transition of fire to new areas.

Combined formulations
The most popular in impregnation technology are combined solutions, including antiseptics, biocides, flame retardants, water-repellent substances that can penetrate into the deepest layers. They can handle any lumber, especially timber, boards for beams, floors, wall cladding. The Senezh impregnation is known for its densification of the structure of the tree, creates a hydrophobic film on it and seriously extends the life of the material.

Deep impregnation methods
Industrial technology is complex and virtually impossible to reproduce at home. To impregnate wood, a special autoclave type installation is required, in which the composition will be supplied under pressure in a vacuum of 0.07–009 MPa. The duration of the process is 3-6 hours.
With your own hands, you can impregnate in the following ways:
- Dipping. Lumber is dipped into a container with an impregnate, aged in it from 2 hours to 7 days (depending on thickness), then it is carefully dried.
- Diffuse method. The drug is mixed with sand 5: 1. This mass is sprinkled with boards, timber, and then wrapped in film. After 10 days, the wood will be ready to dry, before which the film is removed.
to contents ↑
Surface treatment
The effectiveness of such methods is much lower, because the deep layers of wood will remain unprotected. Nevertheless, many masters practice surface types of wood impregnation, which reduce the rate of damage to material by rot, prevent the settlement of pests:
- Staining. The solution is applied by brush, roller to horizontally laid lumber. Typically, the agent penetrates to a depth of 3-5 mm. To enhance efficiency, it is recommended to process 2-3 times.
- Rubbing. It is used on wood with a rough surface that is difficult to paint. The solution is rubbed with durable tampons, sponges in 2-3 layers.
- Spraying. It is used for floors, facades, hard-to-reach areas. The penetration depth of the solution is minimal - up to 1-2 mm.

Manufacturer's Suggestions
On sale there are Russian and foreign impregnation impregnations. The most popular brands are Tex, Senezh, Healthy House, Olympus, Optimist, which are produced in Russia. From foreign compositions in demand:
- Belinka;
- Pinotex;
- Tikkurilla;
- Dufa;
- Maxima;
- Alpina.

Wood processing can be made to order, this service is practiced by many medium and large logging companies. Cost per cubic meter of impregnated wood amounts to 18-30 thousand rubles or more, depending on the type of tree. The high cost is due to a serious benefit for the user, because the service life of buildings and structures will increase significantly.





